logrotate 是一个 linux 系统日志的管理工具。可以对单个日志文件或者某个目录下的文件按时间 / 大小进行切割,压缩操作;指定日志保存数量;还可以在切割之后运行自定义命令。
logrotate 是基于 crontab 运行的,所以这个时间点是由 crontab 控制的,具体可以查询 crontab 的配置文件 /etc/anacrontab。 系统会按照计划的频率运行 logrotate,通常是每天。在大多数的 Linux 发行版本上,计划每天运行的脚本位于 /etc/cron.daily/logrotate。
/etc/cron.daily
#!/bin/sh # skip in favour of systemd timer if [ -d /run/systemd/system ]; then exit 0 fi # this cronjob persists removals (but not purges) if [ ! -x /usr/sbin/logrotate ]; then exit 0 fi /usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf EXITVALUE=$? if [ $EXITVALUE != 0 ]; then /usr/bin/logger -t logrotate "ALERT exited abnormally with [$EXITVALUE]" fi exit $EXITVALUE
原理
logrotate 是怎么做到滚动日志时不影响程序正常的日志输出呢?
- create:mv+create 执行完之后,通知应用重新在新文件写入
- 重命名正在输出日志文件,因为重命名只修改目录以及文件的名称,而进程操作文件使用的是 inode,所以并不影响原程序继续输出日志;
- 创建新的日志文件,文件名和原日志文件一样,注意,此时只是文件名称一样,而 inode 编号不同,原程序输出的日志还是往原日志文件输出;
- 最后通过某些方式通知程序,重新打开日志文件;由于重新打开日志文件会用到文件路径而非 inode 编号,所以打开的是新的日志文件;
- copytruncate:把正在输出的日志拷 (copy) 一份出来,再清空 (trucate) 原来的日志;清空操作比较快,但如果日志文件太大,那么复制就会比较耗时,从而可能导致部分日志丢失,不过这种方式不需要应用程序的支持
- 将当前正在输出的日志文件复制为目标文件,此时程序仍然将日志输出到原来文件中,此时,原文件名也没有变。
- 清空日志文件,原程序仍然还是输出到预案日志文件中,因为清空文件只把文件的内容删除了,而 inode 并没改变,后续日志的输出仍然写入该文件中。
Linux文件操作机制
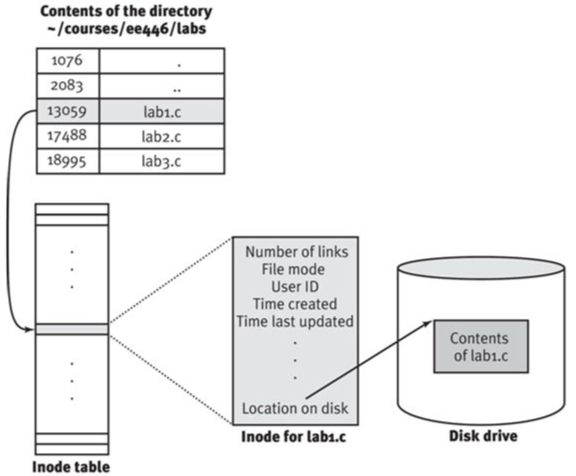
Linux 文件系统里文件和文件名的关系如下图:
目录也是文件,文件里存着文件名和对应的 inode 编号。通过这个 inode 编号可以查到文件的元数据和文件内容。文件的元数据有引用计数、操作权限、拥有者 ID、创建时间、最后修改时间等等。文件件名并不在元数据里而是在目录文件中。因此文件改名、移动,都不会修改文件,而是修改目录文件。
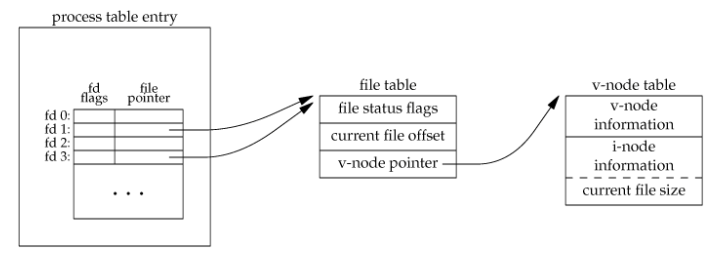
进程每新打开一个文件,系统会分配一个新的文件描述符给这个文件。文件描述符对应着一个文件表。表里面存着文件的状态信息(O_APPEND/O_CREAT/O_DIRECT...)、当前文件位置和文件的 inode 信息。系统会为每个进程创建独立的文件描述符和文件表,不同进程是不会共用同一个文件表。正因为如此,不同进程可以同时用不同的状态操作同一个文件的不同位置。文件表中存的是 inode 信息而不是文件路径,所以文件路径发生改变不会影响文件操作。
Logrotate配置
执行文件: /usr/sbin/logrotate
主配置文件: /etc/logrotate.conf
自定义配置文件: /etc/logrotate.d/*.conf
修改配置文件后,不需要重启服务,本质上logrotate是一个可执行文件,不是以deamon运行
# see "man logrotate" for details
# rotate log files weekly
# 每周轮换日志文件
weekly
# use the adm group by default, since this is the owning group of /var/log/syslog.
# 默认使用 adm 组,因为这是 /var/log/syslog 的拥有组。
su root adm
# keep 4 weeks worth of backlogs
# 保持4周的积压量
rotate 4
# create new (empty) log files after rotating old ones
# 在轮换旧的日志文件后创建新的(空的)日志文件
create
# use date as a suffix of the rotated file
# 使用日期作为旋转后的文件的后缀
#dateext
# uncomment this if you want your log files compressed
# 如果你想让你的日志文件被压缩,请取消这个注释
#compress
# packages drop log rotation information into this directory
# 软件包将日志轮换信息放入此目录
include /etc/logrotate.d
# system-specific logs may be also be configured here.
# 系统特定的日志也可以在这里配置。/etc/anacrontab
# /etc/anacrontab: configuration file for anacron
# See anacron(8) and anacrontab(5) for details.
SHELL=/bin/sh
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
MAILTO=root
# the maximal random delay added to the base delay of the jobs
RANDOM_DELAY=45
# the jobs will be started during the following hours only
START_HOURS_RANGE=3-22
#period in days delay in minutes job-identifier command
1 5 cron.daily nice run-parts /etc/cron.daily
7 25 cron.weekly nice run-parts /etc/cron.weekly
@monthly 45 cron.monthly nice run-parts /etc/cron.monthly如果机器没有关机,默认的logrotate(配置文件里设置的是cron.daily)一般会在每天的3点05分到3点50分之间执行;
真实的延迟时间是 RANDOM_DELAY + delay in minutes;
如果在3-22这个时间段内服务器处于关机状态,则logrotate会在机器开机5分钟后执行分割日志的操作;
Logrotate运行
用法: logrotate [OPTION...] <configfile>
-d, --debug #Don't do anything, just test and print debug messages
#不做任何事情,只是测试和打印调试信息
-f, --force #Force file rotation
#强制旋转文件
-m, --mail=command #Command to send mail (instead of `/usr/bin/mail')
#发送邮件的命令(而不是`/usr/bin/mail')
-s, --state=statefile #Path of state file
#状态文件的路径
-v, --verbose #Display messages during rotation
#显示旋转过程中的信息
-l, --log=logfile #Log file or 'syslog' to log to syslog
#日志文件或 "syslog "来记录到syslog。
--version Display version informationdebug 模式:指定 [-d|--debug]
logrotate -d <configfile>
并不会真正进行 rotate 或者 compress 操作,但是会打印出整个执行的流程,和调用的脚本等详细信息。
verbose 模式: 指定 [-v|--verbose]
logrotate -v <configfile>
会真正执行操作,打印出详细信息(debug 模式,默认是开启 verbose)
state:指定一个状态文件,此文件记录logrotate上次运行时所看到和执行的操作,以便指导他下次运行时要执行的操作
Logrotate参数
/var/log/log_file {
monthly
rotate 5
compress
delaycompress
missingok
notifempty
create 644 root root
postrotate
/usr/bin/killall -HUP rsyslogd
endscript
}- monthly: 日志文件将按月轮循。其它可用值为
daily,weekly或者yearly。 - rotate 5: 一次将存储 5 个归档日志。对于第六个归档,时间最久的归档将被删除。
- compress: 在轮循任务完成后,已轮循的归档将使用 gzip 进行压缩。
- delaycompress: 总是与 compress 选项一起用,delaycompress 选项指示 logrotate 不要将最近的归档压缩,压缩 将在下一次轮循周期进行。这在你或任何软件仍然需要读取最新归档时很有用。
- missingok: 在日志轮循期间,任何错误将被忽略,例如 “文件无法找到” 之类的错误。
- notifempty: 如果日志文件为空,轮循不会进行。
- create 644 root root: 以指定的权限创建全新的日志文件,同时 logrotate 也会重命名原始日志文件。
- postrotate/endscript: 在所有其它指令完成后,postrotate 和 endscript 里面指定的命令将被执行。在这种情况下,rsyslogd 进程将立即再次读取其配置并继续运行。
常见配置参数
- daily :指定转储周期为每天
- weekly :指定转储周期为每周
- monthly :指定转储周期为每月
- dateext:归档旧版本的日志文件,添加一个每日扩展名,如YYYMMDD,而不是简单地添加一个数字。扩展名可以使用dateformat选项进行配置
- dateformat:只允许使用%Y %m %d和%s指定器。默认值是-%Y%m%d,由这种格式产生的日期戳必须是词法可排序的(即先是年,然后是月,然后是日。例如,2001/12/01
- rotate count :指定日志文件删除之前转储的次数,0 指没有备份,5 指保留 5 个备份
- tabooext [+] list:让 logrotate 不转储指定扩展名的文件,缺省的扩展名是:.rpm-orig, .rpmsave, v, 和~
- missingok:在日志轮循期间,任何错误将被忽略,例如 “文件无法找到” 之类的错误。
- size size:当日志文件到达指定的大小时才转储,bytes (缺省) 及 KB (sizek) 或 MB (sizem)
- compress: 通过 gzip 压缩转储以后的日志
- compresscmd:指定使用哪个命令来压缩日志文件
- uncompresscmd:指定使用哪个命令来解压缩日志文件。默认是gunzip
- nocompress: 旧版本的日志文件不会被压缩
- copytruncate:用于还在打开中的日志文件,把当前日志备份并截断
- nocopytruncate: 备份日志文件但是不截断
- create mode owner group : 转储文件,使用指定的文件模式创建新的日志文件
- nocreate: 不建立新的日志文件
- delaycompress: 和 compress 一起使用时,转储的日志文件到下一次转储时才压缩
- nodelaycompress: 覆盖 delaycompress 选项,转储同时压缩。
- errors address : 专储时的错误信息发送到指定的 Email 地址
- ifempty :即使是空文件也转储,这个是 logrotate 的缺省选项。
- notifempty :如果是空文件的话,不转储
- mail address : 把转储的日志文件发送到指定的 E-mail 地址
- nomail : 转储时不发送日志文件
- olddir directory:储后的日志文件放入指定的目录,必须和当前日志文件在同一个文件系统
- noolddir: 转储后的日志文件和当前日志文件放在同一个目录下
- prerotate/endscript:在转储以前需要执行的命令可以放入这个对,这两个关键字必须单独成行
- sharedscripts:如果指定了sharedscripts,那么无论有多少日志与通配符模式相匹配,脚本都只运行一次,整个模式都会传递给它们。然而,如果模式中没有一个日志需要轮换,脚本就根本不会被运行。如果脚本以错误方式退出,剩下的动作将不会对任何日志执行;
运行示例
/home/torch/koko.log {
su ceasia ceasia #权限
daily
dateext
rotate 14
compress
missingok
copytruncate
sharedscripts
notifempty
}
# debug运行
ceasia@dev-32:~$ logrotate -df /etc/logrotate.d/koko
WARNING: logrotate in debug mode does nothing except printing debug messages! Consider using verbose mode (-v) instead if this is not what you want.
reading config file /etc/logrotate.d/koko
Reading state from file: /var/lib/logrotate/status
Allocating hash table for state file, size 64 entries
Handling 1 logs
rotating pattern: /home/torch/koko.log forced from command line (14 rotations)
empty log files are not rotated, old logs are removed
considering log /home/torch/koko.log
Creating new state
Now: 2023-01-31 15:27
Last rotated at 2023-01-31 15:00
log needs rotating
rotating log /home/torch/koko.log, log->rotateCount is 14
dateext suffix '-20230131'
glob pattern '-[0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9]'
glob finding old rotated logs failed
copying /home/torch/koko.log to /home/torch/koko.log-20230131
truncating /home/torch/koko.log
compressing log with: /bin/gzip
# 强制运行
ceasia@dev-32:~$ sudo logrotate -fv /etc/logrotate.d/koko
reading config file /etc/logrotate.d/koko
Reading state from file: /var/lib/logrotate/status
Allocating hash table for state file, size 64 entries
Handling 1 logs
rotating pattern: /home/torch/koko.log forced from command line (14 rotations)
empty log files are not rotated, old logs are removed
switching euid to 1000 and egid to 1000
considering log /home/torch/koko.log
Now: 2023-01-31 15:31
Last rotated at 2023-01-31 15:00
log does not need rotating (log is empty)
switching euid to 0 and egid to 0
# 设置crontab
01 0 * * * /usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.d/koko --state /opt/jumpserver/koko/data/logs/logrotate-state
/var/log/nginx/*.log {
daily
dateext
missingok
rotate 31
compress
delaycompress
notifempty
create 0640 nginx root
sharedscripts
postrotate
/bin/kill -USR1 `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid 2>/dev/null` 2>/dev/null || true
endscript
}